Efficient solid-liquid separation is a critical part of industrial filtration, particularly in industries such as mining, food processing, wastewater treatment, and pharmaceuticals. When it comes to achieving high-quality filtration results, two of the most widely used components are filter press belts and filter cloths. Both play integral roles in various types of filtration equipment, but they differ in design, performance, application, and cost-effectiveness.
By examining their structure, advantages, limitations, and applications, we aim to help plant managers, process engineers, and procurement teams determine the best fit for their operations.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding Filter Press Belts and Filter Cloths
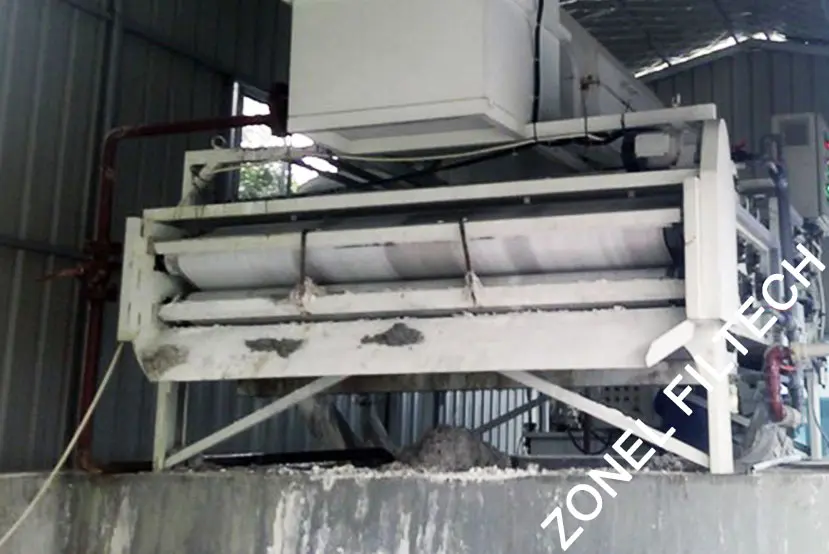

What Are Filter Press Belts?
Filter press belts are continuous looped fabrics used in belt filter presses, a type of mechanical dewatering equipment. The belt presses apply a combination of gravity and mechanical pressure to remove water from slurry or sludge. The belt itself acts as the filtration medium.
Typically made from high-strength polyester or polypropylene, filter press belts feature woven or non-woven structures that allow water to pass while retaining solids. They are tensioned and rotated between rollers to compress the slurry.
What Are Filter Cloths?
Filter cloths are flat, fabric-based filtration media used in plate and frame filter presses or membrane filter presses. Each filter cloth is cut to size and fitted over filter plates, forming chambers where slurry is pumped in and dewatered under high pressure.
They are composed of synthetic materials including nylon, polyester, polypropylene, and other fibers, either woven or non-woven. Filter cloths come in a wide variety of weaves, thread counts, and pore sizes to match different filtration needs.
Structural and Functional Differences
| Feature | Filter Press Belts | Filter Cloths |
| Design | Continuous loop, long-width fabric | Cut-to-size panels fitted to plates |
| Installation | Installed in belt press machines; looped and tensioned | Mounted on each individual filter plate |
| Motion | Continuously moving during operation | Static during filtration cycle |
| Operation Mode | Continuous dewatering | Batch filtration |
| Cleaning | Washed continuously with spray bars | Manually or automatically cleaned during cloth change or wash cycle |
Performance and Efficiency
Filtration Efficiency
Filter cloths typically offer higher precision in filtration due to their ability to be tightly matched to specific particle sizes and filtration needs. They are ideal for fine filtration tasks.
Filter press belts, while excellent for general sludge dewatering, may not achieve the same level of precision. However, they perform very well in continuous processes where high throughput is more important than extreme clarity.
Throughput and Speed
Filter press belts excel in continuous operations. Belt presses can process large volumes of slurry without interruption, making them ideal for wastewater treatment and industrial sludge processing.
Conversely, filter cloths are employed in batch operations. While they can handle high pressure and provide better dryness levels, the cycle times are longer due to the press open/close cycle and cake discharge.
Solids Capture and Cake Dryness
Filter cloths can achieve better cake dryness, often exceeding 35-45% depending on the slurry composition and press pressure. Membrane filter presses can further squeeze out moisture by inflating membranes against the cake.
Filter press belts generally produce lower dryness, usually in the range of 15-30%. However, this is typically sufficient for sludge conditioning before disposal or incineration.
Maintenance and Durability
Filter Press Belts
Pros | Cons |
|
|
Filter Cloths
Pros | Cons |
|
|
Cost Considerations
| Cost Factor | Filter Press Belts | Filter Cloths |
| Initial Cost | Higher due to material length and loop design | Lower per unit, but more units needed |
| Operational Cost | Lower in high-volume continuous use | Higher due to manual intervention and downtime |
| Replacement Frequency | Moderate (6–12 months) | More frequent depending on slurry type (3–6 months) |
| Cleaning Cost | Lower due to integrated spray system | Higher due to manual or automated cleaning systems |
Application Suitability
Ideal Uses for Filter Press Belts
- Municipal and industrial sludge dewatering
- Pulp and paper processing
- Food and beverage byproduct dewatering (e.g., fruit pulp, brewery waste)
- Textile dyeing wastewater
- Chemical plant wastewater treatment
These industries value the continuous operation, high capacity, and moderate cake dryness offered by belt filter presses.
Ideal Uses for Filter Cloths
- Pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and fine materials filtration
- Mining and metallurgy (e.g., tailings dewatering)
- Food processing for high-purity filtration (e.g., starch, sugar, juice clarification)
- High-pressure filtration applications (e.g., membrane filter presses)
- Situations requiring precise particle retention and dry cake discharge
Filter cloths are favored in industries that demand batch precision, high cake dryness, and customized filtration profiles.
Customization and Compatibility
Filter Press Belts
- Available in different permeabilities, weave types, and air permeability rates.
- Can be edge-reinforced to prevent fraying.
- Optional features: clipper seams, spiral links, and endless woven designs.
Filter Cloths
- Can be customized in fabric type, pore size, weave pattern, surface treatments, and gasket types.
- Compatible with various plate sizes, chamber depths, and filtration types (cake-washing, core-blow, etc.).
- Can be tailored for chemical resistance, heat resistance, or antistatic properties.
Environmental and Regulatory Considerations
Environmental regulations require wastewater discharge and sludge disposal to meet specific criteria. Therefore, choosing the right filtration media can affect compliance.
Filter press belts are more eco-friendly for large-scale sludge management due to reduced manual handling, automated cake removal, and minimized wash water usage.
Filter cloths, although capable of producing drier cakes (which reduce disposal weight), may use more energy and water due to frequent washing and cloth changes.
Which Is Better for Your Operation?
Choosing between filter press belts and filter cloths depends on several factors:
| Consideration | Better Option |
| Continuous operation | Filter Press Belts |
| High filtration precision | Filter Cloths |
| Batch control & pressure | Filter Cloths |
| Large-scale sludge processing | Filter Press Belts |
| Maximum cake dryness | Filter Cloths |
| Low manual intervention | Filter Press Belts |
| Low initial cost | Filter Cloths |
| Customized applications | Filter Cloths |
If your operation is high-volume, continuous, and focused on moderate dryness with minimal labor, filter press belts are likely the better option.
If your operation requires high pressure, fine filtration, and high cake solids, especially in batch processes, filter cloths provide better results.
Conclusion
Both filter press belts and filter cloths play crucial roles in industrial filtration, but their effectiveness depends on your specific operational needs. Filter press belts shine in continuous, high-throughput environments, offering convenience and durability. Filter cloths, however, are indispensable for batch precision, achieving high cake dryness, and filtering finer particles.
By understanding the structural, functional, and application differences between the two, plant managers and engineers can make informed decisions that enhance process efficiency, reduce operational costs, and ensure compliance with environmental regulations.
Whether you’re optimizing an existing filtration setup or planning a new installation, evaluating your slurry characteristics, desired output, and plant infrastructure will help you choose the most effective filtration solution for your operation.
